Explain Different Types of Keys in Dbms With Examples
The minimal set of attributes that can uniquely identify a tuple is known as a candidate key. Before we move to the actual discussion let us see different types of keys and a list of topics to be covered in the blog Different types of keys.

Different Types Of Keys In Dbms Webeduclick
There are four various types of keys Primary Key Candidate Key Foreign Key and Super Key.

. It specially identifies each record in a table. Surrogate keys are just simple sequential number. A super key has the uniqueness property but not necessarily the irreducibility property.
Here I come to my topic ie. The different types of attributes are as follows. Keys uniquely identify records or a combination of records from huge database tables.
Key attribute has clearly different value for each element in an entity set. The entity student ID is a key attribute because no other student will have the same ID. Lets look at each of them separately.
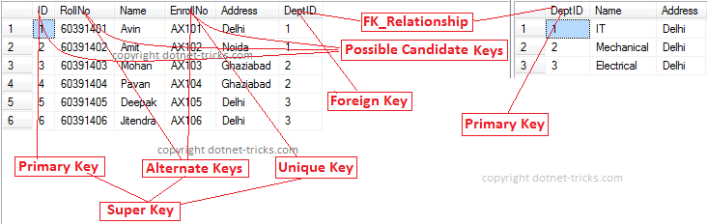
Candidate Super Primary Foreign Key Types with Example. DBMS vs RDBMS Types of Keys in DBMS. There can be numerous keys present in a table which can be seen in the Personal Information table.
3 rows The different types of keys in DBMS are. The objective of this blog is to make you familiar with different types of keys with examples and how they can be used within a database app. Alternate Key Out of all candidate keys only one gets selected as primary key remaining keys are known as alternate or secondary keys.
Key Differences with Example. Clustered vs Non-clustered Index. The Keys are as follows.
Of a student is unique in relation. It is a type of functional dependency that occurs when non-prime attributes are partially dependent on part of Candidate keys. A candidate key can be a combination of more than one columnsattributes.
This is the first key that helps in identifying a single instance of an entity in a distinct manner. Composite Key A key that consists of more than one attribute to uniquely identify rows also known as records tuples in a table is called composite key. For example if Roll_number is unique in relation STUDENT then the set of attributes.
Primary key is a candidate key that is most appropriate to become the main key for any table. Super Key Candidate Key Primary Key Foreign Key Composite Key Lets discuss one by one all of the five keys. The database key types can be broadly grouped into two groups.
Different Types of Keys in Relational Model. Whats the Difference Between SQL and NoSQL. The first group of keys include unique keys and the second group is non-unique keys.
DBMS KEYS A Short Seminar On Submitted To- Deepak Paranjape Sir. It can be divided into smaller sub parts each sub part can form an independent attribute. There can be more than one candidate key in a relation.
A database key is said be unique when it has a unique value for each row that is tuple record instance. DBMS has Five types of Keys in it and they all has different functionality. This attribute represents the main characteristic of an entity ie.
To understand these in detail read further. CREATE TABLE Orders OrderID int NOT NULL OrderNumber int NOT NULL PersonID int PRIMARY KEY OrderID FOREIGN KEY PersonID REFERENCES PersonsPersonID. Candidate Key A super key with no redundant attribute is known as candidate key.
Super Key is a set of properties within a table. They are crucial for the arrangement of tables in the database. 7 Different Types of Database Keys Explained with Example Keys play a very important role in DBMS.
There are two types of participation constraints. There are broadly seven types of keys in DBMS. A candidate key is a special case of a super key.
For example in SQL Server or Sybase database system contain an artificial key that is known as Identity. For Example STUD_NO in STUDENT relation. The attributes of student entity are as follows.
Sample of key attribute. A primary key is a column of a table or a set of columns that helps to identify every record present in that table. It is a key that can uniquely identify each record in a table.
The value of the Candidate Key is unique and non-null for every tuple. In the above example we have applied not null on three columns ID name and age which means whenever a record is entered using insert statement all three columns should contain a value. Explain Database Scheme and Its.
The relationship can be between two strong entity or a strong entity and a weak entity. NOTE- Before proceeding further Kindly note-. Database keys are also useful in establishing a.
Surrogate keys are only used to act as a primary key. There can be any number of candidate keys in a table. Different Types Of Keys in DBMS- There are following 10 important keys in DBMS- Super key.
For the table Student we can make the student_id column as the primary key. In the employee tableImg3 if manager details are to be fetched for an employee multiple results are returned when searched with EMP_ID in order to fetch one result EMP_ID and PROJECT_ID together are considered as. Branch_Id is a Surrogate Key in Branch_Info table and Student_Id is a Surrogate key of Student_Information table.
Name FirstName MiddelName LastName. The set of properties like roll no name class age sex is. Candidate key is a unique case of super key.
Candidate Key - The candidate keys in a table are. Depending upon the type of entity participating in the relationship the participation can be partial or total.

Types Of Keys In Relation Primary Key Alternate Key Composite Key Lecture38 Dbms Youtube

Comments
Post a Comment